Foot drop may also be called drop foot, dorsiflexion weakness, peroneal nerve paresis, peroneal nerve palsy or dorsal flexor disorder. All these terms indicate a condition in which the sufferer has problems lifting their foot. This results in a typical gait known as the ‘cock walk’, in which the knee is raised unnaturally high to prevent the toes dragging on the ground during walking.
In this article, we explain the causes and symptoms of foot drop and outline treatment options as well as ways of preventing the disorder.
Foot drop: causes and symptoms
In a healthy person, walking is a fully automatic process. We usually don’t give a second thought to the remarkable interaction of muscles, bones, nerves and tendons that makes these movements possible. It’s a different story when this automatic process no longer functions correctly. If a person suffers from foot drop, even walking slowly becomes a huge effort. But what causes foot drop?

When does peroneal nerve paralysis occur?
Normally, movement impulses are sent from the brain to the spinal cord, from where the impulses reach the neural pathways. If this process is interrupted at any point, the impulses cannot be correctly transmitted and processed.
In the case of foot drop, the peroneal nerve is affected. This extends from the thigh to the knee, where it splits into two branches that continue into the foot. The actual restriction of the nerve may originate in the leg itself or in the spine or brain. If there is paralysis or damage to the nerve, the brain impulses that are supposed to lift the leg so that a person can walk are not correctly transmitted. This results in the typical problems with walking.
Causes of damage to the foot dorsiflexor nerve include:
- stroke
- traumatic brain injury
- multiple sclerosis
- spinal cord injury
- complications after a hip replacement
- slipped disc
Foot drop: typical symptoms of the condition
The main symptom of peroneal nerve palsy is an affected gait, characterised by the above-mentioned cock walk. Due to the paralysis of the dorsal flexor nerve, the sufferer is not able to lift their foot when they walk and then roll off it, in order to take a step. Instead, the toe of the dropped foot often hangs downwards or even drags over the ground. To prevent this, the patient tries to keep the foot as far above the ground as possible. They do this by raising the knee unusually high when walking – as if they were on a stair climber.
Due to the incorrect gait and abnormal action when walking, foot drop may cause further problems in the long run. These include pain in the hips as well as in the pelvis, knees or back. In addition, the muscles, tendons and bones are put under a lot of strain due to the cock walk, and the leg or the foot may feel numb.
Foot drop leads to various problems in everyday life
The main problems associated with foot drop are difficulties in walking. A consequence of this is frequent stumbling, which can also lead to dangerous falls and serious injuries. The paralysis can also result in serious difficulties at work. Even the drive to work can become very difficult in the presence of untreated foot drop and should be avoided if possible in order to protect the sufferer and other road users from accidents. However, there are ways to treat peroneal nerve paralysis that make it possible to live with the condition.

Can foot drop be cured?
Foot drop is usually the result of another illness or injury. If the foot becomes paralysed, the first step is to find out what is causing it. If the original illness is treated, the peroneal nerve palsy symptoms may also subside. However, the paralysis itself can also be treated if required. To find the right cure that is tailored precisely to the treatment of the individual’s symptoms, early intervention by doctors, physiotherapists or orthopaedic technicians is important.
Exercises to strengthen the muscles
There are various ways to treat foot drop. The different treatment options should always be accompanied by physiotherapy, if the patient’s condition allows.
There are many exercises, such as bare-foot walking or use of a spiky massage ball, which can stimulate the musculature of the foot and blood flow. Another aim of physiotherapy is to strengthen the musculature of the foot and leg. If the paresis has been caused by a slipped disc, the back should also be strengthened. The physiotherapist will decide which exercises are most suitable for treating the symptoms of individual patients.
Fabric supports to help relieve foot drop
In the case of a mild paresis of the dorsal flexor nerve, fabric supports or textile orthotics may help. These fabric supports wrap around the affected foot and ensure more stability when walking. The foot and the ankle joint are stabilised, ideally meaning that the patient stumbles and goes over on their ankle less often. In the long term, this can help normalise the gait.

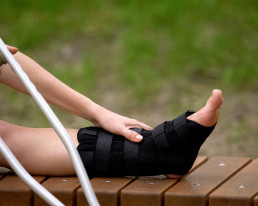
Ankle foot orthoses (AFOs) to correct the gait
In the case of moderately severe peroneal nerve paresis, ankle foot orthoses are often used. These are lightweight, padded splints made of carbon fibre. The splints are available with different levels of rigidity and can be individually adapted to the patient’s requirements. Orthotics offer the foot better stability than fabric supports and help sufferers to lift and roll off the foot. The additional support can also help prevent muscle fatigue when walking and correct the gait in the long term.
Treatment using electrical impulses
Another method of treating foot drop is the use of electrical impulses. This is known as ‘functional electrical stimulation’ (FES). It involves the use of a cuff with electrodes that is worn below the knee. The electrodes send electrical impulses to the paralysed peroneal nerve, which in turn sends them to the dorsal flexor muscle. The impulses help to raise the foot. This treatment method is only feasible if the peroneal nerve is not irreparably damaged, but only paralysed or impaired.
Surgery to correct foot drop
In some cases, an operation can help to correct paralysis of the dorsal flexor nerve. This applies particularly if the nerve is restricted by pressure from the surrounding tissue. Using surgery to relieve the pressure can help the nerve to regenerate and to remain healthy in the long term.
How can peroneal nerve palsy be prevented?
As already mentioned, foot drop is usually a secondary complaint, whose cause can be found in another illness. The best way to prevent foot drop is therefore also to prevent other illnesses as far as possible. This involves a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, enough sleep and sufficient exercise.
To prevent foot drop as a result of slipped discs or hip injuries, precautions and safety measures should be taken – particularly at work – in order to protect the skeleton, the musculature and the nerves.
These measures include:
- preventive occupational medical examinations by the company doctor in order to ensure early detection and treatment of illnesses that may cause foot drop
- ergonomic office furniture to ensure people can sit properly at their workstation
- regular occupational safety training to make employees aware of the possible health risks associated with strenuous tasks in the workplace and recommended treatment options

Foot drop: conclusion
Foot drop can lead to serious difficulties in everyday life. Even walking slowly becomes a strenuous activity. The impaired function of the leg means that frequent stumbling is likely, leading to an increased risk of falling and injury.
The disorder can be caused by a variety of pre-existing conditions. Therefore, when foot drop occurs, the cause must be found before further action can be taken and treatment determined. In the best-case scenario, however, foot drop can be prevented by avoiding predisposing conditions or treating them properly and promptly.