
Standards and Directives
Of course, based on regulation (EU) 2016/425 on personal protective equipment (PPE) our products meet all the necessary standards, and not just that – we always require that little bit more from our products. This ensures the extra safety that our customers – rightly – expect from us.
EN 166 is being replaced by EN ISO 16321
For more than 20 years, the EN 166 standard has defined all of the requirements and standards for safety eyewear within the European Union and the United Kingdom. EN 166 is now being replaced by EN ISO 16321. EN ISO 16321 comes into force in November 2025 and with it some changes regarding the requirements and labelling of safety spectacles.
Further information on the background and detailed changes can also be found on our blog.
EN ISO 16321 – briefly explained
Like EN 166, EN ISO 16321 defines all the requirements for eye protection products. These are divided into three sub-standards:
- EN ISO 16321-1: general requirements; UV, sunglare and IR filters
- EN ISO 16321-2: welding protection filters
- EN ISO 16321-3: mesh visors
It is designed for possible internationalisation so that countries outside the European Union can also recognise the validity of the standard in the future.
Markings on lenses in accordance with EN ISO 16321

| U | UV protection filter |
| G | Sunglare filter |
| W | Welding protection filter |
| R / RR | Infrared protection filter |
| + L | Signal light detection (optional, can be additionally certified for each filter) |
| Marking | Light transmittance | Available uvex tints |
| U1,2 | 74.4 – 100 % | AR, clear, amber |
| G1 | 43.2 – 80 % | CBR65, silver mirror 53% |
| G2 | 17.8 – 43.2 % | CBR23, grey 23% |
| G3 | 8 – 17.8 % | Grey 12%, silver mirror 12%, polavision |
| W1,7 | 43.2 – 58.1 % | Welding shade level 1,7 |
| W3 | 8.5 – 17.8 % | Welding shade level 3 |
| W5 | 1.2 – 3.2 % | Welding shade level 5 |
| RL1,7 | 43.2 – 58.1 % | Infrared protection IR-ex level 1,7 |
| RL3 | 8.5 – 17.8 % | Infrared protection IR-ex level 3 |
| RL5 | 1.2 – 3.2 % | Infrared protection IR-ex level 5 |
| None | Drop ball test in accordance with EN ISO 16321 (basic requirement) |
| C | Low-energy impact (45 m/s or 162 km/h) |
| D | Medium-energy impact (80 m/s or 288 km/h) |
| E | High-energy impact (120 m/s or 432 km/h) |
| HM* | High-mass impact (500 g steel projectile, drop height 1.27 m) |
| T* | Tested under extreme temperatures (-5°C/+55°C) |
| K | Surface resistance to damage by small particles in accordance with EN ISO 16321 (scratch resistance) |
| N | Resistance to fogging in accordance with EN ISO 16321 |
| 7 | Protection against radiant heat |
| 9 | Protection against molten metal and hot solids |
| CH | Chemical resistance |
Markings on frames in accordance with EN ISO 16321

| None | Drop ball test in accordance with EN ISO 16321 (basic requirement) |
| C | Low-energy impact (45 m/s or 162 km/h) |
| D | Medium-energy impact (80 m/s or 288 km/h) |
| E | High-energy impact (120 m/s or 432 km/h) |
| HM* | High-mass impact (500 g steel projectile, drop height 1.27 m) |
| T* | Tested under extreme temperatures (-5°C/+55°C) |
| 3 | Protection against liquids (drops and splashes) |
| 4 | Protection against large dust particles with a grain size of > 5 μm |
| 5 | Protection against gases, vapours, smoke, fumes and fine dust particles with a grain size of < 5 μm |
| 6 | Protection against high-pressure liquid flows |
| 7 | Protection against radiant heat (visors only) |
| 8 | Protection against short-circuit electric arcs (visors only) |
| 9 | Protection against molten metal and hot solids (visors only) |
| CH | Chemical resistance |
| 1-S | Small, European test head |
| 1-M** | Medium, European test head (standard) |
| 1-L | Large, European test head |
| 2-S | Small, Asian test head |
| 2-M | Medium, Asian test head |
| 2-L | Large, Asian test head |
* Optional
** 1-M is the standard. If only 1-M has been tested, this does not have to be marked on the frame or on the packaging
DIN EN 166 – Personal eye protection
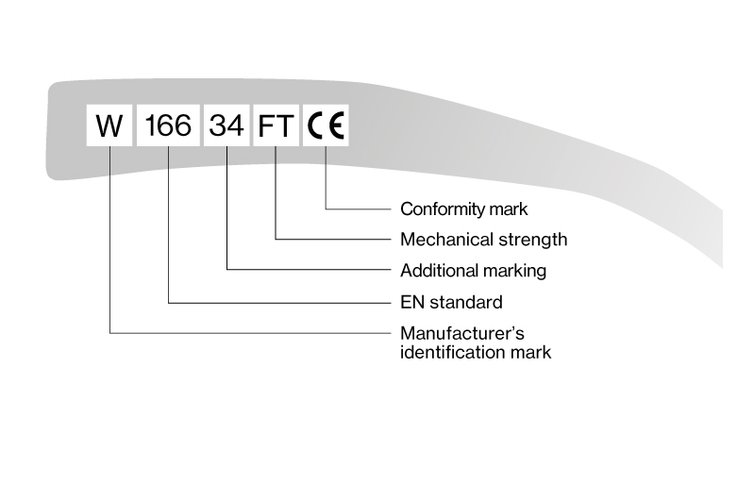
The European standard DIN EN 166 describes all personal eye protection requirements in general. Safety glasses in accordance with DIN EN 166 consist of a frame and lenses, which are classified in the following standards into safety lenses and lenses with a filter effect.
Labelling in accordance with DIN EN 166
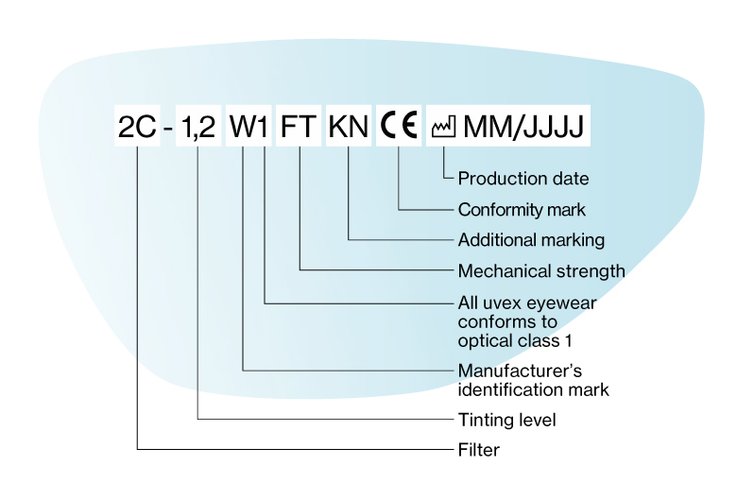
Technical information on safety eyewear lenses are given in the following order in accordance with EN 166:
- protection class (filters only)
- manufacturer mark
- optical class (except for ancillary lenses)
- certification mark (if applicable)
- symbol for mechanical strength
- symbol for non-adherence of molten metal
Marking on lenses in accordance with EN 166
| 2 | UV protection filter (EN 170) |
| 2C/3 | UV protection filter with colour recognition (EN 170) |
| 4 | IR protection filter (EN 171) |
| 5 | Sunglare filter for industrial use (EN 172) |
| 6 | Sunglare filter with infrared requirement |
| AR | 1.2 (Light transmittance 74.4–100%) |
| clear | 1.2 (Light transmittance 74.4–100%) |
| amber | 1.2 (Light transmittance 74.4–100%) |
| CBR65 | 1.4 (Light transmittance 58.1–80%) |
| silver mirror 53% | 1.7 (Light transmittance 43.2–58.1%) |
| CBR23 | 2.5 (Light transmittance 17.8–29.1%) |
| grey 23% | 2.5 (Light transmittance 17.8–29.1%) |
| polavision | 3.1 (Light transmittance 8–17.8%) |
| grey 14% | 3.1 (Light transmittance 8–17.8%) |
| silver mirror 12% | 3.1 (Light transmittance 8–17.8%) |
| none | Minimum robustness (filters only) |
| S | Increased robustness |
| F | Low-energy impact (45 m/s or 162 km/h) |
| B | Medium-energy impact (120 m/s or 432 km/h) |
| A | High-energy impact (190 m/s or 684 km/h) |
| T | Tested under extreme temperatures (-5°C/+55°C) |
| K | Surface resistance to damage by small particles in accordance with EN 168 (scratch-resistance) |
| N | Resistance to fogging in accordance with EN 168 |
| 8 | Protection against short-circuit electric arc |
| 9 | Protection against molten metal and hot solids |
Marking on frame in accordance with EN 166
| none | General use |
| 3 | Protection against liquids (drops and splashes) |
| 4 | Protection against large dust particles with a grain size of > 5 μm |
| 5 | Protection against gases, vapours, smoke, fumes and fine dust particles with a grain size of < 5 μm |
| 8 | Protection against short-circuit electric arc |
| 9 | Protection against molten metal and hot solids |
| none | Minimum robustness (filters only) |
| S | Increased robustness |
| F | Low-energy impact (45 m/s or 162 km/h) |
| B | Medium-energy impact (120 m/s or 432 km/h) |
| A | High-energy impact (190 m/s or 684 km/h) |
| T | Tested under extreme temperatures (-5°C/+55°C) |
DIN EN 169 – Filters for welding and related techniques
In relation to special product requirements for eye protection, the EN 169 standard defines protection levels and transmittance requirements for lens filters intended to protect employees during:
- light flame cutting
- hard soldering
- welding
- arc gouging
- plasma cutting
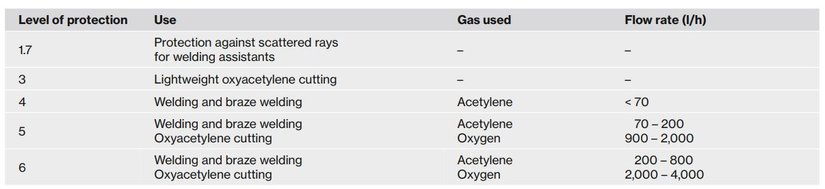
Labelling and protection levels for welding filters in accordance with standard EN 169
Welding filters must be permanently marked on the edge. The first number refers to the protection class of the safety eyewear. Depending on the procedure, higher electrical currents require higher protection classes in accordance with DIN EN 169.
DIN EN 172 – Sun glare filters for industrial use
DIN EN 172 is a special standard for personal eye protection and describes the required physical properties of filters used to reduce sun glare in industrial use. These properties include, for example, mechanical and optical characteristics and requirements of the sun glare filters.
To use the sun glare filters in industrial use, the general requirements for personal eye protection in accordance with DIN EN 166 must also be fulfilled. Depending on the area of use, sun glare filters in accordance with DIN EN 172 can be used either as filters in spectacles or as individual filters.
Thanks to innovative technologies, uvex sun glare filters in accordance with DIN EN 172 offer perfect colour perception combined with optimal protection.
DIN EN 171 – Infrared protection filter
The effect of infrared radiation on human tissue can be harmful. Since it is not immediately noticeable, infrared radiation can increase the risk of permanent eye damage, such as cataracts.
Levels of infrared protection and recommendations for use according to EN 171
| Level of protection | Recommended use in accordance with EN 171 |
| 4-1,7 | average temperature of the radiation source up to 1090°C* |
| 4-2 | average temperature of the radiation source up to 1110°C (forges) |
| 4-3 | average temperature of the radiation source 1190°C (glass blowing)* |
| 4-4 | average temperature of the radiation source 1290°C (foundries) |
| 4-5 | average temperature of the radiation source 1390°C (steel foundries)* |
| 4-6 | average temperature of the radiation source 1510°C (iron foundries) |
* available in the uvex portfolio



































