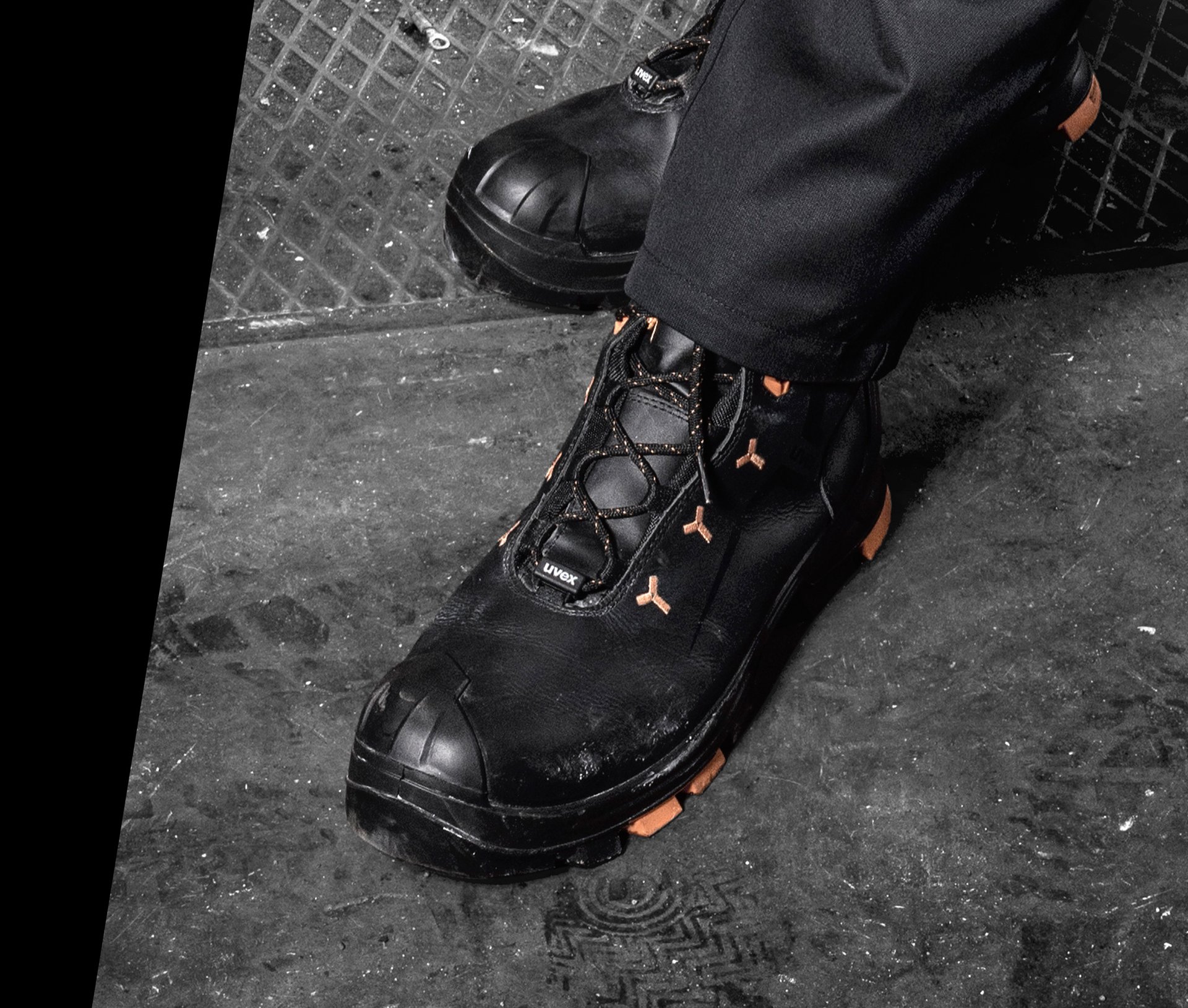
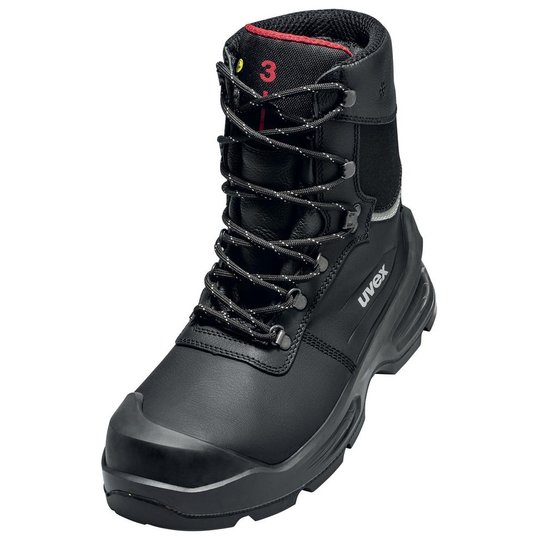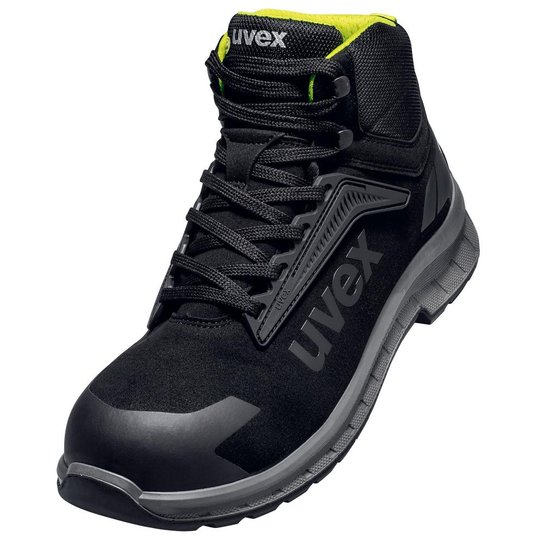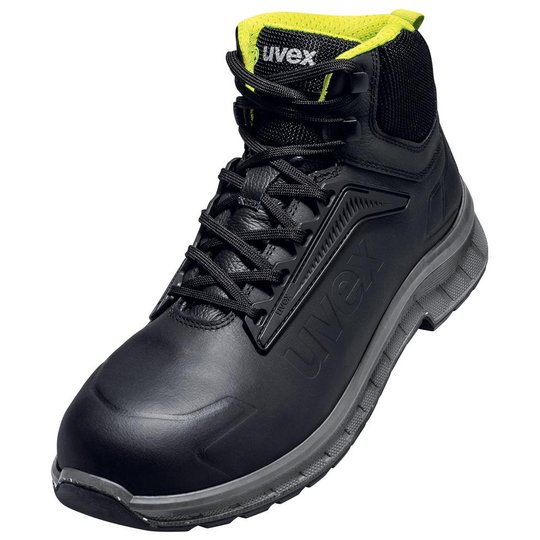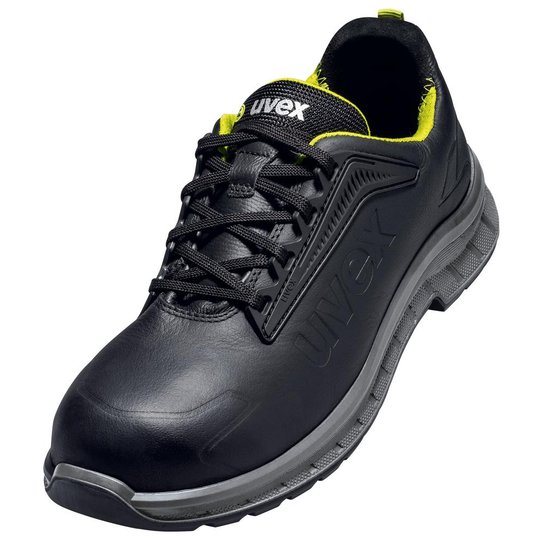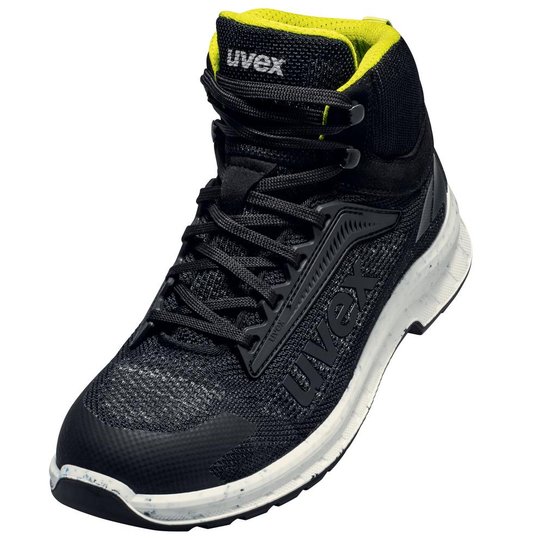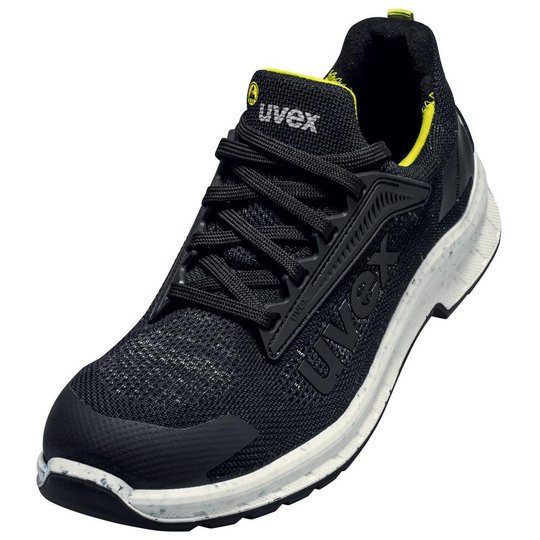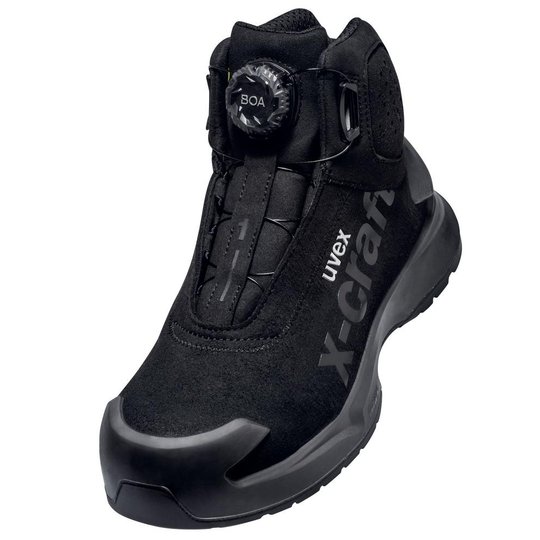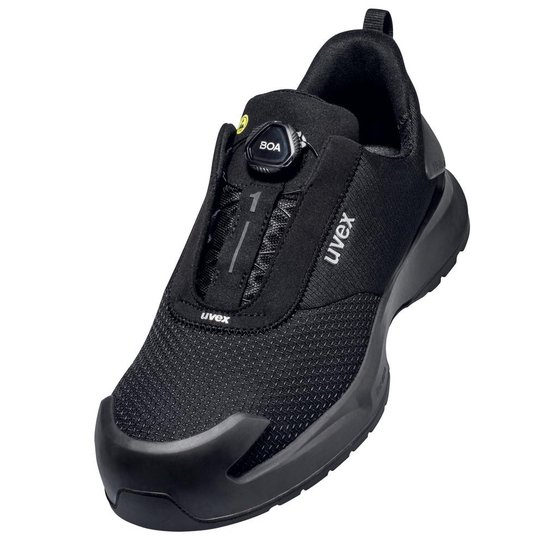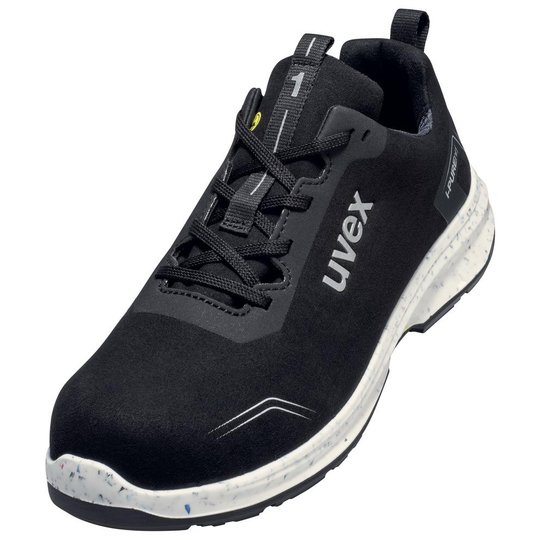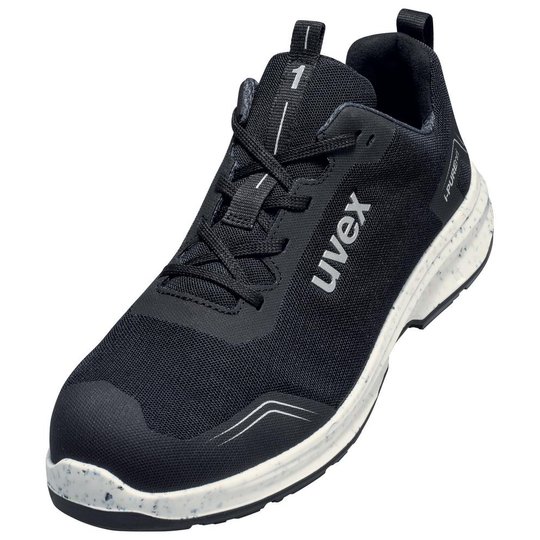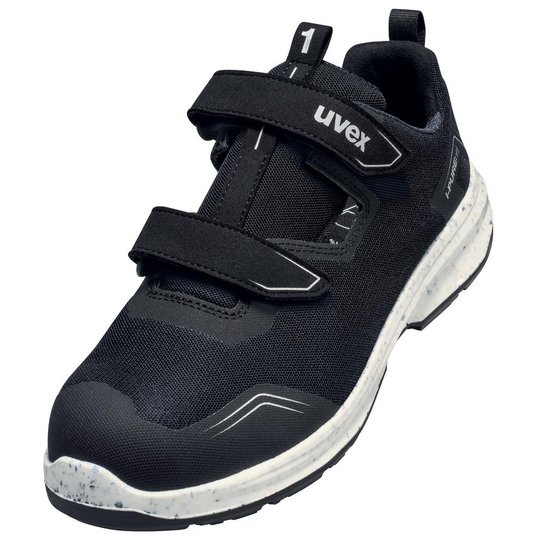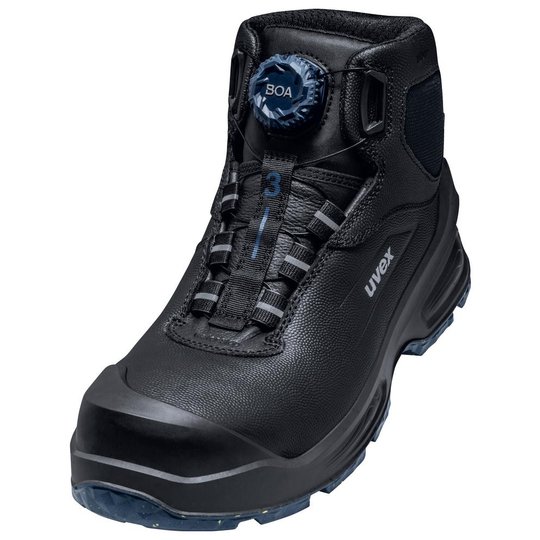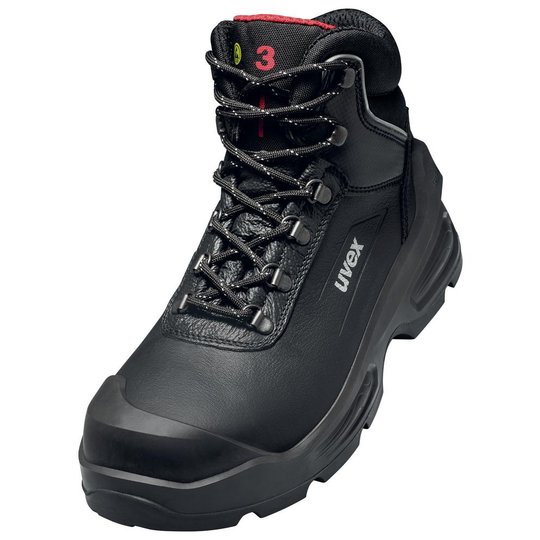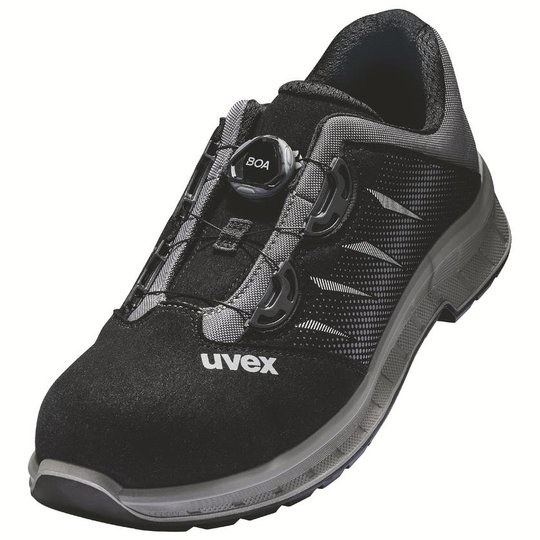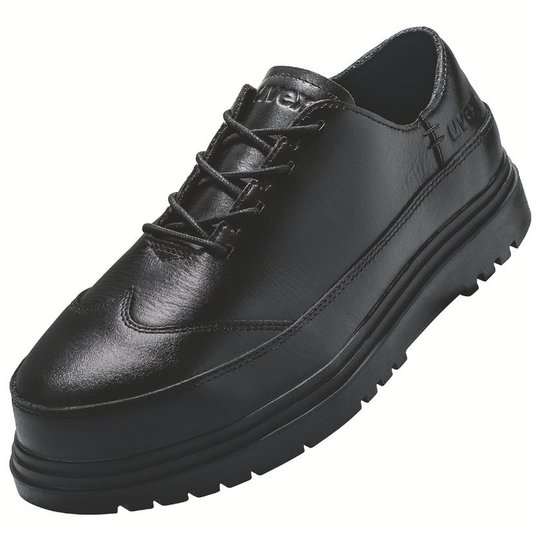
ESD safety shoes from uvex – for protecting electronic components
ESD stands for electrostatic discharge. In the working environment this involves the discharge of static charge caused by friction or contact with the surrounding area. Even voltages above 100 volts can seriously damage sensitive components or disrupt their function. ESD safety shoes from uvex dissipate these charges in a controlled way and therefore protect electronic devices and your working environment. The main feature of ESD-certified safety shoes is the sole – consisting of the insock, insole and outsole.
FILTER
When do I need ESD safety shoes
ESD safety shoes are required in all industries where sensitive electronic components such as electronic chips or devices are handled. They should be worn in “electrostatic protected areas” (EPA) in the following industries:








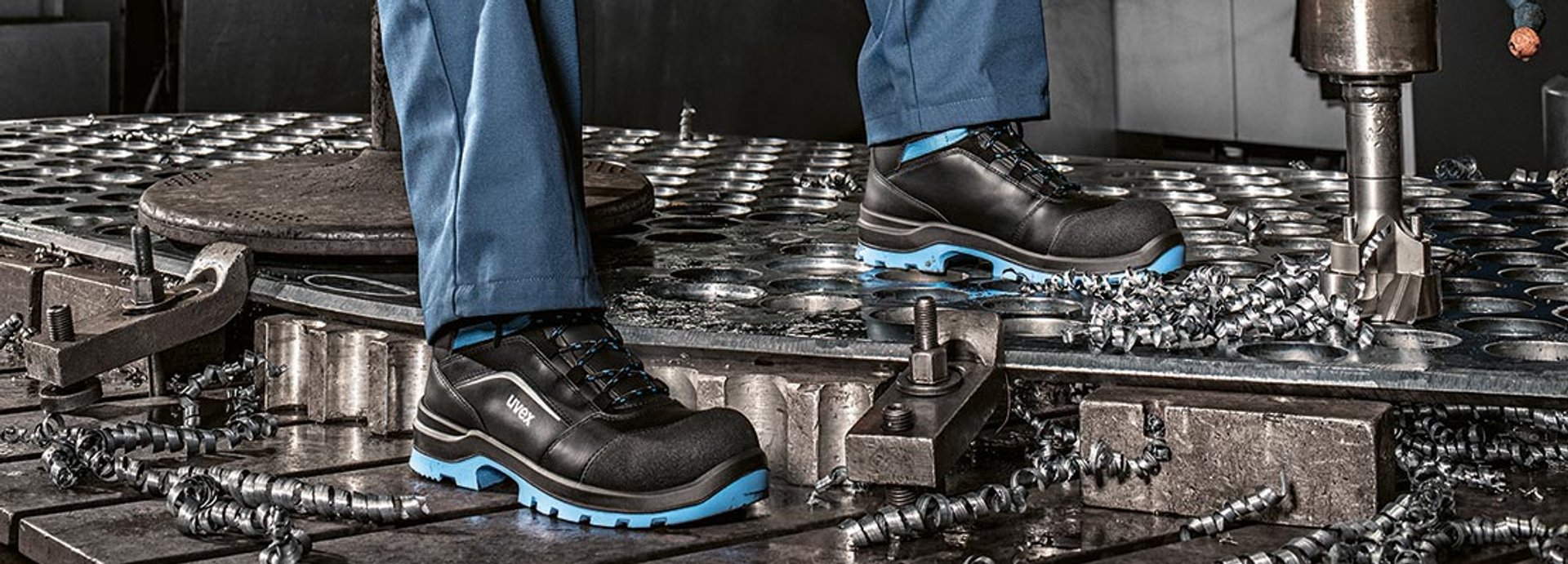
Which standards and requirements do ESD work shoes have to meet?
ESD work shoes for men and women must meet the standards DIN EN 61340-5-1 and DIN EN 61340-4-3:
- DIN EN 61340-5-1: This standard assesses the resistance of the charge that is dissipated to the ground by people via their shoes in order to safely control electrostatic charges.
- DIN EN 61340-4-3: Here, the resistance is tested under laboratory conditions, as factors such as temperature and humidity can influence the conductivity.
The resistance in both cases must be between 100 kiloohms (105 ohms) and 100 megaohms (108 ohms). An ESD shoe certified in accordance with EN 61340-5-1 can be recognised by the yellow ESD mark.


What is the difference between ESD shoes and anti-static safety shoes?
ESD and anti-static safety shoes have in common that they both reduce electrostatic charge or dissipate it in a controlled manner. The decisive difference is in the scope of protection:
Anti-static shoes

From safety class S1 and higher, safety shoes must be anti-static. This requirement is fulfilled if the measured resistance is in the range between 100 kiloohms (105 ohms) and one gigaohm (109 ohms). It protects the wearer against hazards that can occur in connection with electrostatic charge and reduces the risk of materials or vapours igniting in potentially explosive atmospheres.
ESD shoes

The ESD range defined according to EN 61340-5-1 outlines a specific demarcation within the anti-static range and protects especially sensitive electronic components. The resistance is between 100 kiloohms (105 ohms) and 100 megaohms (108 ohms).
This means that ESD shoes are always anti-static, the reverse is not true. Shoes with a resistance greater than one gigaohm (109 ohms) are considered electrically insulating according to the standard. If the resistance is less than 100 kiloohms (105 ohms), they are considered conductive.

Safety shoes with ESD certification from uvex
You can find more information on the topics ESD – how to prevent electrostatic charge and the difference to anti-static and The difference between anti-static and ESD using the example of safety shoes in our x-pertblog. If you are interested in ESD gloves, we recommend the articles Work gloves with touchscreen and ESD function – Industry 4.0 requirements for safety gloves and A new electrostatic test standard for safety gloves.




























































